About PVC
What is PVC?
Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is one of the most widely used polymers in the world. Because it is so versatile, PVC is used extensively in a broad range of industrial, technical and everyday applications. PVC is an intrinsically low-carbon plastic: 57% of its molecular weight is accounted for by chlorine derived from common salt, 5% by hydrogen and 38% by carbon. It is recyclable and is increasingly being recycled. The European PVC industry has been working hard to boost collection and improve recycling technologies.
Several recent eco-efficiency and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies of major PVC applications have shown that in terms of energy use and GWP (global warming potential), the performance of PVC is comparable to that of alternative products. In many cases, PVC applications resulted in both lower total energy consumption and lower CO2 emissions.
A unique advantage of PVC is the possibility is its ability to enable innovation: its formula can be changed to produce new applications with improved safety and eco-efficiency, while maintaining the same level of technical performance.
PVC everywhere
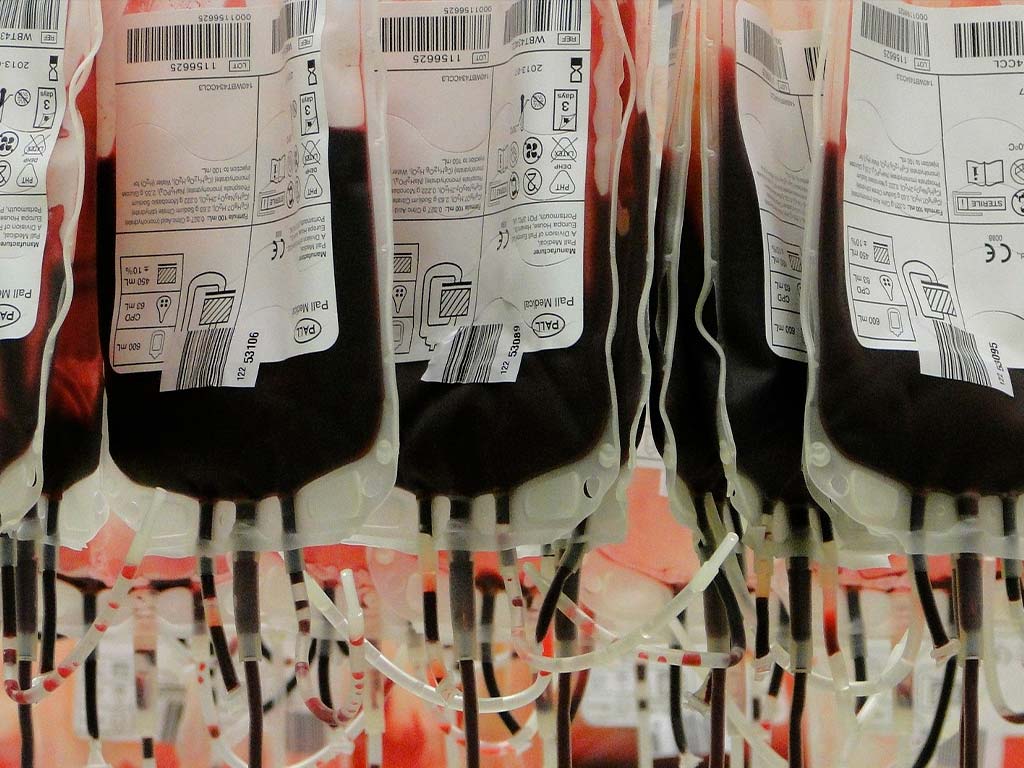
Due to its light weight, durability and stability, PVC can offer energy, cost and material efficiency gains for sectors such as building and construction, water distribution, health and transportation. Whether it is rigid or flexible, PVC helps to make cars lighter and resistant against corrosion, it enables windows to last longer, allows fresh water delivery through the use of durable piping, and stores blood to save and improve people's lives.
Three value chain platforms, each dedicated to communicate about the use of PVC in key application areas are organized by the European Council of Vinyl Manufacturers (ECVM): PVCMed Alliance for PVC in healthcare, PVC4Pipes for PVC in piping systems and PVC4Cables for PVC in cables.
Below are some of the most common PVC applications.






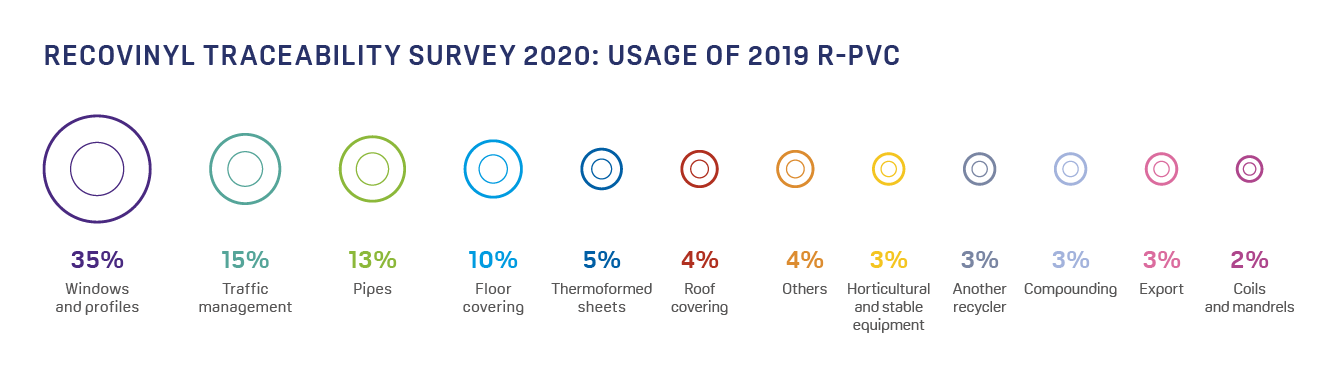
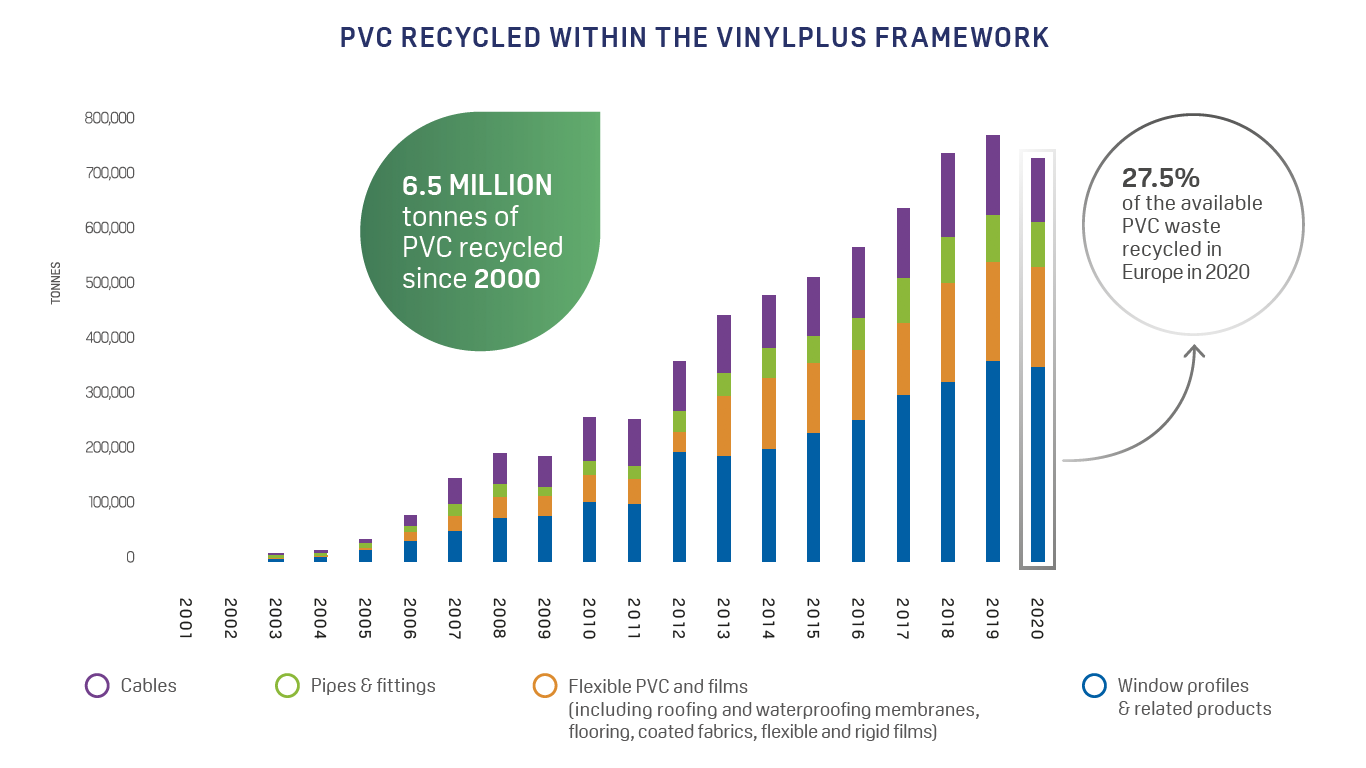
Is PVC being recycled?
PVC can be recycled repeatedly up to 8 times depending on the application, because the recycling process does not measurably decrease the chain length of PVC molecules. The European industry has been working very hard to boost collection of PVC waste and to optimize recycling technologies. The goal is to minimize waste and energy use while boosting the percentage of recyclate in new products.
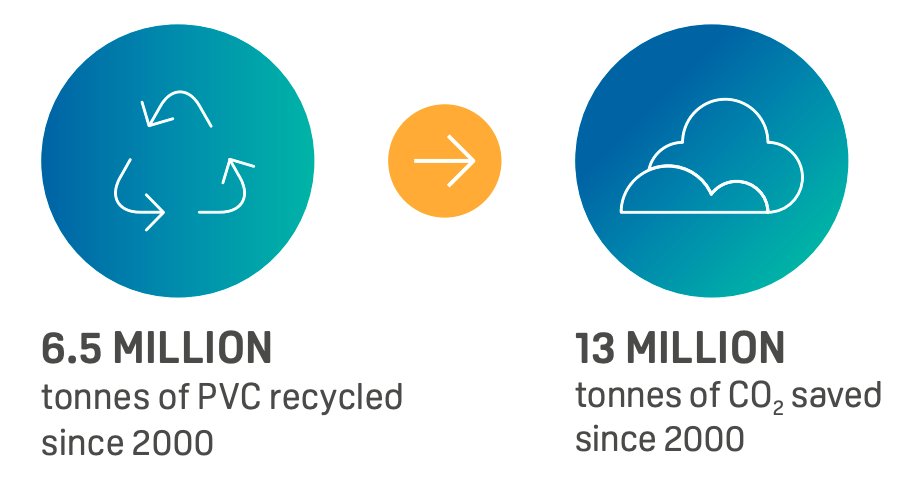
In 2020, 730,000 tonnes of PVC waste were recycled within the VinylPlus framework. Since 2000, more than 6.5 million tonnes of PVC have been recycled into new products.

Where can recycled PVC be found?
Nowadays, recycled PVC can be mostly found in window profiles, flexible applications and piping.